Discover the top 10 innovative building materials that significantly reduce embodied carbon, paving the way for more sustainable construction practices.
Understanding Embodied Carbon in Construction
Embodied carbon refers to the greenhouse gas emissions generated throughout the lifecycle of building materials, from extraction and manufacturing to transportation, installation, maintenance, and disposal. Unlike operational carbon emissions, which are associated with the energy consumption of buildings, embodied carbon is locked into the materials themselves.
As buildings become more energy-efficient and rely increasingly on renewable energy sources, operational emissions are decreasing. This shift places a greater emphasis on embodied carbon, making it a larger share of a building’s total carbon footprint. Selecting low embodied carbon building materials is therefore essential for anyone aiming to design and construct more sustainable buildings.
The Importance of Low Embodied Carbon Materials
In the quest for sustainability, reducing embodied carbon is crucial. Buildings contribute significantly to global carbon emissions, and a large portion of this comes from the materials used. By choosing low embodied carbon materials, we can significantly cut down the overall carbon footprint of construction projects.
Moreover, focusing on low embodied carbon materials supports the principles of a circular economy, promotes the use of renewable resources, and often enhances the indoor environmental quality. This holistic approach not only benefits the environment but also contributes to healthier living and working spaces.
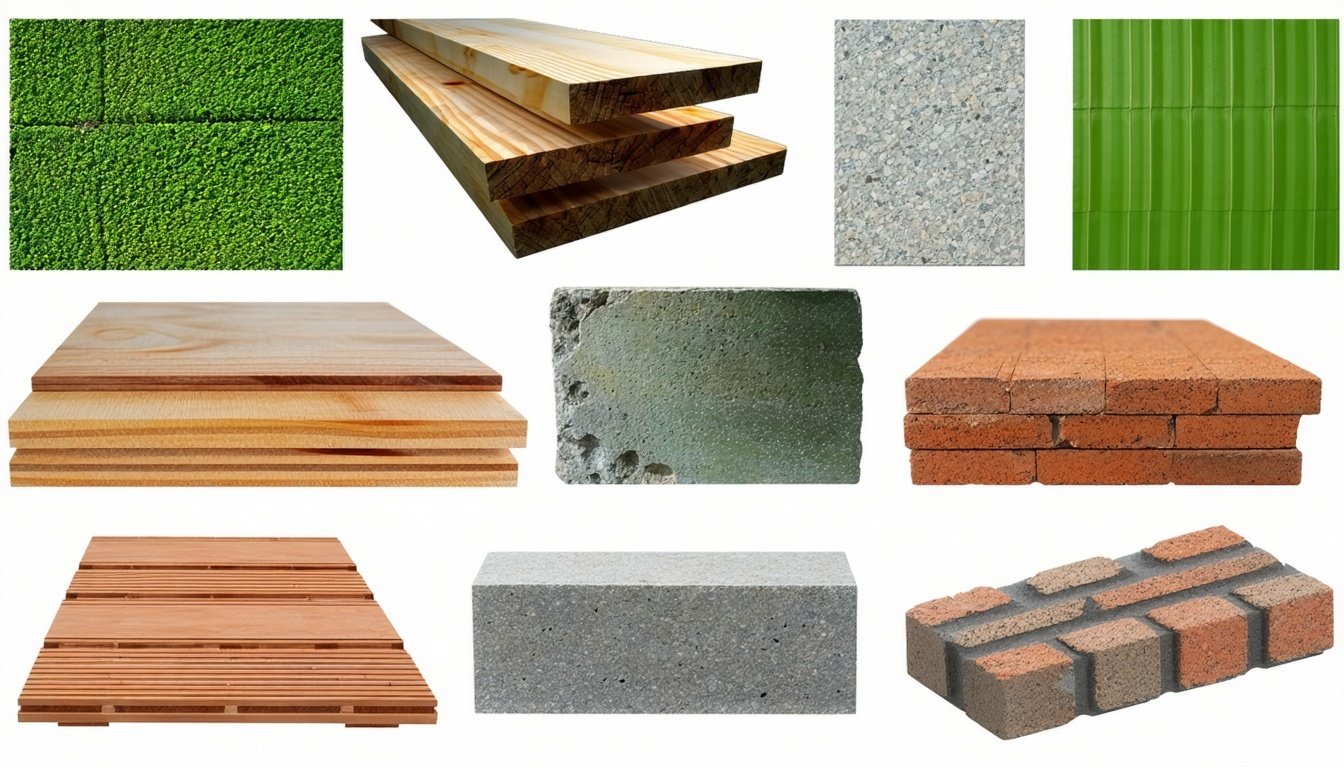
Top 10 Low Embodied Carbon Building Materials
1. Biobased Flooring Products: Made from natural materials like cork, bamboo, or linoleum, these flooring options have a much lower carbon footprint compared to traditional materials like vinyl or carpet.
2. Recycled Bricks: Utilising bricks made from recycled construction waste reduces the need for new raw materials and cuts down on the energy-intensive manufacturing process.
3. Green Concrete: Incorporating industrial by-products like fly ash or slag, green concrete reduces the need for cement, which is a major source of carbon emissions in conventional concrete.
4. Mass Timber: Engineered wood products such as cross-laminated timber (CLT) sequester carbon and provide a sustainable alternative to steel and concrete in structural applications.
5. Hempcrete: A biocomposite material made from the inner fibres of the hemp plant, hempcrete is a carbon-negative material, meaning it absorbs more CO2 than it emits during its lifecycle.
6. Wood Fibre Insulation: Derived from sawmill residues, wood fibre insulation offers excellent thermal properties while being a renewable and biodegradable option compared to synthetic insulations.
7. Green Steel: Produced using renewable energy sources and innovative manufacturing techniques, green steel significantly reduces the carbon footprint associated with traditional steel production.
8. Rammed Earth: Utilising locally sourced earth materials, rammed earth construction has minimal processing requirements and offers excellent thermal mass properties.
9. Reclaimed Wood: Sourcing wood from old buildings or other structures reduces the demand for new lumber and preserves the carbon sequestered in the original wood.
10. Recycled Metal Roofing: Made from recycled aluminium or steel, these roofing materials cut down on the energy required for production and reduce landfill waste.
Benefits of Using Low Embodied Carbon Materials
Using low embodied carbon materials in construction projects offers numerous benefits. Firstly, it significantly reduces the overall carbon emissions of a project, contributing to global efforts to combat climate change. Secondly, many of these materials support circular economy principles by utilising recycled or renewable resources.
Additionally, low embodied carbon materials often enhance indoor environmental quality by reducing exposure to harmful chemicals and improving air quality. This can lead to healthier and more comfortable living and working environments.
How to Choose the Right Materials for Your Project
To prioritise low embodied carbon building materials in your projects, start by consulting Environmental Product Declarations (EPDs), which provide detailed information about the environmental impact of materials. Using embodied carbon databases can also help you compare different materials and make informed decisions.
Look for certified or biobased products that meet recognised standards, and consider the entire lifecycle of the materials you choose. By taking these steps, architects, builders, and sustainability professionals can make significant strides towards more sustainable construction practices.